Zegar
Stronę tą wyświetlono już: 4663 razy
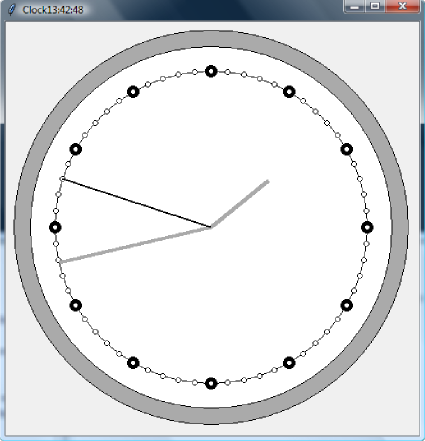
Kolejny prosty programik napisany w Pythonie 3+ z wykorzystaniem modułu tkinter, którego celem jest nic innego jak tylko wyświetlanie bieżącego czasu. Oto kod tego programu:
Poniżej zamieszczam screen programu.

Tytuł:
Python w analizie danych. Przetwarzanie danych za pomocą pakietów pandas i NumPy oraz środowiska Jupyter. Wydanie III
Autor:
Wes McKinney

Tytuł:
Machine learning, Python i data science. Wprowadzenie
Autor:
Andreas Müller, Sarah Guido

Tytuł:
Python zorientowany obiektowo. Programowanie gier i graficznych interfejsów użytkownika
Autor:
Irv Kalb

Tytuł:
Python na start! Programowanie dla nastolatków
Autor:
Michał Wiszniewski

Tytuł:
Sztuczna inteligencja w finansach. Używaj języka Python do projektowania i wdrażania algorytmów AI
Autor:
Yves Hilpisch

Tytuł:
Python w zadaniach. Programowanie dla młodzieży. Poziom podstawowy
Autor:
Urszula Wiejak, Adrian Wojciechowski

Tytuł:
Python i praca z danymi. Przetwarzanie, analiza, modelowanie i wizualizacja. Wydanie III
Autor:
Avinash Navlani, Armando Fandango, Ivan Idris

Tytuł:
Black Hat Python. Język Python dla hakerów i pentesterów. Wydanie II
Autor:
Justin Seitz, Tim Arnold

Tytuł:
Python z życia wzięty. Rozwiązywanie problemów za pomocą kilku linii kodu
Autor:
Lee Vaughan

Tytuł:
Python i AI dla e-commerce
Autor:
Sebastian Kondracki